Do you Know How does your Email really work? What pathways are used and Which protocols are used and how its gets delivered to raja@domain.com and not to raje@domain.com
Local deliveries:
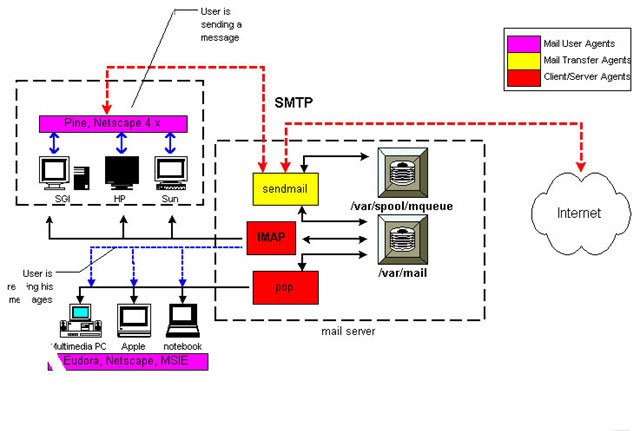
Assume that your Email address is name@domain.com and you are using an Email client like Outlook Or Thunderbird to send and receive Emails.This is known as Mail User Agent(MUA).For sending mails,the MUA uses Simple Mail Transfer Protocol(SMTP).SMTP is also used by Mail Transfer Agent like Gmail.If the user directly Using webmail like Gmail,Yahoo the MUA does not need in this.
Also Read : How to Access your GMail Messages, Calendar and Docs in offline Mode
If the Address in the ‘to’ field has the same domain(xxx@gmail.com and yyy@gmail.com),then MTA search the local Mailboxes(each user has their own mailbox) and then delivers the mail.
The receiver’s Mail Delivery Agent (MDA it is a Server or Outlook) retrieves this Mail using Post Office Protocol(POP3) Or Internet Message Access Protocol(IMAP4).If POP3 is used ,the email message is copied to the local Email client and a copy is or isn’t retained on the server depending on the client settings.If IMAP4 is used,then the copy of the message is always retained on the server.However, this system works only for small networks.
In this case Domains are different,or the sender and receiver both using the Email services like Gmail,Hotmail,an entirely different complicated process takes place.
Read More Gmail backup Tips: How to Backup Your GMail Emails in 5 Ways; Save it for Offline Access
DNS And MX:
In this case the MUA or Web mail connects to the local MTA,Which is operated by ISP(Internet Service Provider).SMTP is used in this connection via Port Number 25.If heavy load occurs,an Email queue is formed,while the MTA processes each mail.MTAs use data in the headers of the Email to ask the Domain Name Servers(DNS) for the route.Typically, a single message would be routed across the multiple MTAs. Since IP addresses are the only thing that computers can understand.The MTA looks at the Domain Name(the part after @)in the DNS to find the Mail Exchange (MX) record for that domain.Before this,domain name resolution has to be done.Starting the top level domains like .org, .edu , .net , .gov(there are many of them).
Let’s consider that the Email address of the recipient is xxx@otherdomain.com. The MX record that is obtained from DNS is actually a prioritized list of servers for otherdomain.com. The mail is progressively channeled via the different MX servers in a decreasing order of priority,until the designated host for the domain is found. MX servers are actually another name for MTAs that receive mail. The last MTA then transfers the mail to the host and it is retrieved by the recipient using the MDA, or accessed through web mail using POP3 or IMAP4.
Format and security:
The format of the Email messages is called MIME(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension).Before MIME, Only Plain text could be sent.MIME specifies how other types of information to be formatted so that they can be sent along with Emails. The mapping between MIME and other formats are done by MDAs and Mail servers.
Email is sent over open channels,which is made it interception.Nowadays, mechanisms like digital and PGP(Pretty Good Privacy) are used so that Email is responsibly secure.However, the way Email is stored and retrieved leaves it open to privacy issues.
MainTerms used in Email Architecture:
Mail User Agent(MUA)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol(SMTP)
Mail Transfer Agent(MTA)
Mail Delivery Agent (MDA)
Post Office Protocol(POP3)
Internet Message Access Protocol(IMAP4)
ISP(Internet Service Provider)
Mail Exchange (MX)
MIME(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension)
PGP(Pretty Good Privacy)